Context: The Gomti River in Lucknow is at risk of becoming ecologically dead due to rising untreated sewage, declining oxygen levels, and increasing faecal coliform levels.
About the Gomti River
Origin
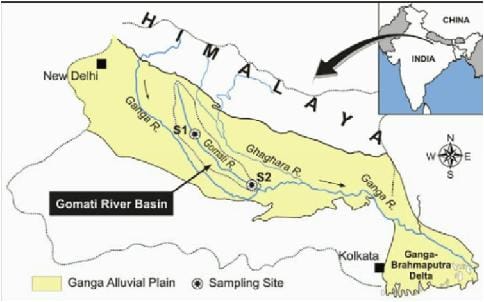
The Gomti River arises from Gomat Taal (Fulhaar Jheel) near Madho Tanda in Pilibhit district, Uttar Pradesh.
Course
It flows entirely through Uttar Pradesh, traversing districts like Lucknow, Sitapur, Sultanpur, Jaunpur, Faizabad, and others, before joining the Ganga River at Kaithi in Ghazipur district.
Length & Basin
- Total Length: Approximately 960 km.
- Drainage Area: Around 18,750 sq km (7,240 sq miles).
- Perennial river with sluggish flow except during the monsoon season.
Major Tributaries
- Sai River
- Chowka River
- Kathina River
- Saryu River
- Sarayan River
Cultural and Religious Significance
- Considered sacred in Hinduism, believed to be the daughter of Rishi Vashishtha.
- Mentioned in the Bhagavata Purana as one of the five transcendental rivers.
- The rare Gomti Chakra shells are found in its sands.
Ecological Risks and Pollution
- Untreated Sewage Inflow: Raw sewage from Lucknow has sharply increased organic load.
- Declining Dissolved Oxygen: Oxygen levels have fallen below thresholds necessary for aquatic life.
- Rising Faecal Coliform: Pathogen counts exceed safe limits, posing health risks.
Conclusion
The Gomti River’s decline underscores urgent need for sewage treatment upgrades, strict effluent monitoring, and community‑driven cleanup initiatives to restore its ecological vitality and preserve its cultural heritage.